02 Feb. 2022 TCD guidelines for assessment of Brain Death in regard of organ transplantations
TCD for instrumental diagnosis and confirmation of Brain Death
Brain Death (BD) diagnosis has become an important topic of ethical discussion about organ donation. TCD for instrumental diagnosis of BD is considered as an additional matter of safety. BD is not confirmed as long as TCD or EEG confirm it instrumentally.
Brain Death diagnostic according to guidelines
The German Transplant Law stipulates requirements of organ removal, which have to match present scientific knowledge.
Therefore, the German medical council (Bundesärztekammer, BÄK) issues guidelines of Brain Death (BD) detection, which structure this process precisely (§ 16 Absatz 1).
Due to the organ donation affair at some German university hospitals in 2012 (Munich, Göttingen and Regensburg), again, BD diagnosis has become an important topic of ethical discussion about organ donation. Both doctors and relatives consider instrumental diagnosis (e.g. TCD or EEG) as an additional matter of safety.
According to the guidelines of the German medical council (BÄK) Brain Death is defined as a condition of irreversible malfunction of cerebrum, cerebellum as well as brainstem. Therefore, circulation and oxygen supply are maintained by mechanical ventilation. Equally, a certain sign of death (e.g. decapitation) establishes confirmation of BD.
Confirmation of Brain Death
Confirmation of Brain Death requires exclusion of: Intoxications, sedative effect of drugs, neuromuscular block (e.g. muscle relaxants), hypothermia, hypoperfusion (circulatory shock) and coma caused by endocrinal or infectious (septic shock) reasons.
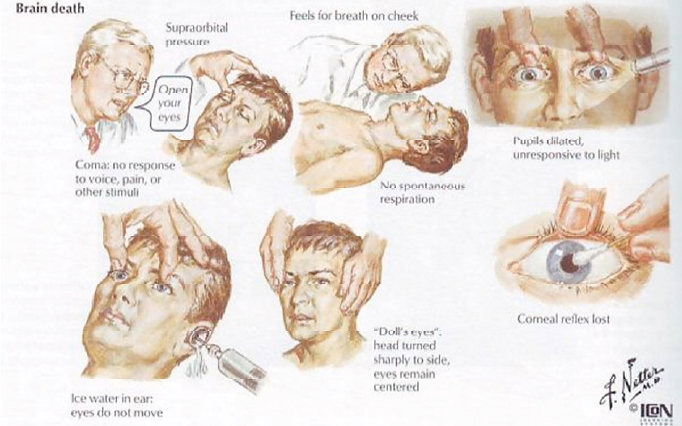
Clinical signs of Brain Death are:
- Coma
- Unresponsive pupils
- Missing oculo-cephalic reflex (eye movement on passive head rotation)
- Loss of corneal reflex
- Loss of reaction on pain stimulus
- Loss pharyngeal reflex
- Loss of spontaneous respiration
Referring to BÄK, all requirements and all clinical signs must apply commonly, which needs to be confirmed within a reasonable time period again. For lesions, which are primarily infratentorial, Brain Death is not confirmed as long as TCD (circulatory arrest) or EEG (zero line) confirm BD instrumentally.
TCD as diagnostic device for Brain Death
Refering to BÄK Brain Death (BD) must be confirmed using two clinical examinations at different times/dates (“within a reasonable period of time”) or by one clinical examination and one additional instrumental diagnostic examination.
- EEG (zero line)
- Evoked potentials (SEP, FAEP)
- Cerebral circulatory arrest confirmed by: a. Transcranial Doppler sonography, b. Brain perfusion scintigraphy, c. Selective arterial angiography (Cave: requirement for examination is an objective possibility of therapeutic intervention)
- High specificity (Literature implies nearly 100%)
- Good sensitivity (Literature demonstrates 75-90%) (Most likely caused by failure of acoustic windows; Can be improved by insonation of carotid siphon.; Can be improved by re-examinations)
- TCD is cheap, can be performed bedside (avoids transport of critical patients) und does not harm.
- Reliable results even in case of intoxication.
- Independent of the location of cerebral lesion (infra- and supratentorial lesions)
Diagnostic criteria for TCD examinations
BÄK: Cerebral circulatory arrest (CCA) is confirmed if Doppler examination of intra- and extra-cranial brain feeding vessels was performed by a certain experienced doctor and following conditions are provided: at least two examinations within a time lag of at least 30 minutes reveal one of following results on both sides:
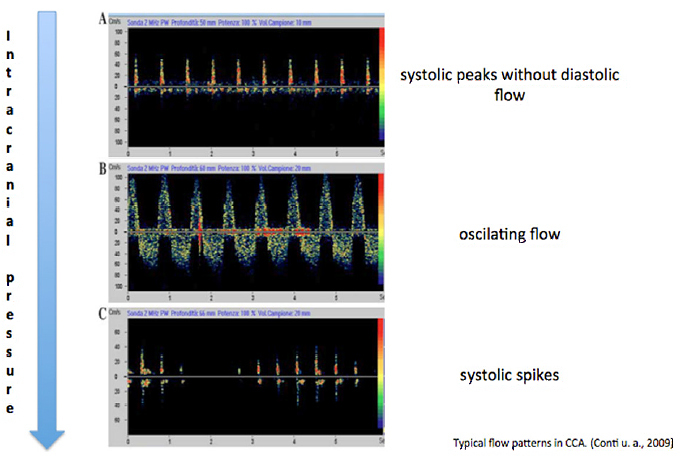
- Biphasic flow (oscillating flow) with equally pronounced orthograde and retrograde components or early systolic peaks, which are less than 50 cm/s, whereas all other intra- and extra-cranial arteries do not show flow signals.
- Missing flow signals in transcranial examination of intracranial arteries confirms circulatory arrest only if the same examinator observed a loss of signal on previously certain derived signals and extra-cranial arteries indicate CCA as well.
Transcranial flow patterns, which confirm brain death.
Modified from Conti et al., 2009.