13 Mrz 2023 Sickle Cell Disease and TCD
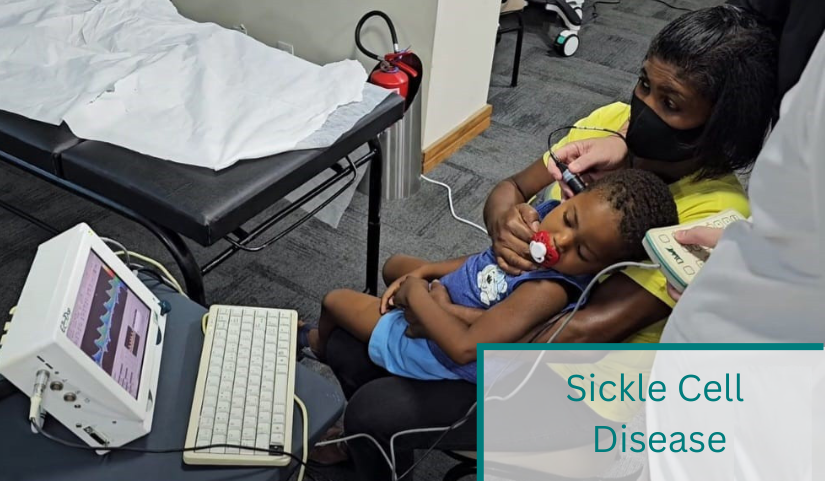
TCD in use with Sickle Cell Disease
Sickle Cell Disease (SCD) is one of the world’s most prevalent genetic diseases and the result of sickle-shaped deformations of the erythrocytes due to a genetic defect. Especially children with Sickle Cell Disease frequently have steno-occlusive lesions in large cerebral arteries and microangiopathic lesions, causing ischemic stroke and silent infarcts that impact on neurocognitive development and quality of life. The disease is mainly found in areas with widespread cases of malaria and occurs from a gene mutation in the children of infected people. Through migration, sickle cell anemia is spreading globally and has become a global public health issue.
TCD Sickle Cell Disease diagnosis, prognosis, and treatment
Stroke is one of the most serious complications that occur in children suffering from sickle cell disease (SCD), affecting approximately 5-10% of children with an incidence peak in the first decade of life. According to current knowledge the stroke recurrence is supposed to be 50-90% in untreated children.
Transcranial Doppler sonography (TCD) is the gold standard to assess blood flow velocities in the vessels of the Circle of Willis in SCD patients and predict the risk of stroke. TCD is highly recommended as a routine screening tool not only for Sickle Cell Disease diagnostics, but also for prognosis and for guiding therapy and treatment: exchange transfusions, hydroxyurea, allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplant, recently approved drugs and new therapeutic options (gene therapy, gene editing).
During an examination with the TCD, the user is given the opportunity to display the highest blood flow velocities and therefore determine the SCD quickly and easily.
Categorized TCD values to reduce stroke risk for children with Sickle Cell Disease
National SCD guidelines recommend that TCD screening should begin at age 2 years and continue annually until at least 16 to 18 years. Categorized TCD values in accordance with the STOP trial(s) (Adam et. al) has become widely used, such as Normal <= 170cm/s; Conditional – between 170 and 199 cm/s and Abnormal >= 200 cm/s. Actual recommendations e.g., of the American Society of Hematology guidelines (2020) suggests strategies for tracking TCD assessments and treatment of children with SCD and abnormal TCD measurements because these children are at extremely high risk for ischemic strokes.
References
What drives transcranial Doppler velocity improvement in paediatric sickle cell anaemia: analysis from the Sickle Cell Clinical Research and Intervention Program (SCCRIP) longitudinal cohort study
Jeremie H. Estepp, Ze Cong, Irene Agodoa, Guolian Kang, Juan Ding, M. Beth McCarville, Jane S. Hankins, Winfred C. Wang; (2022)
Transcranial Doppler screening in Nigerian children with sickle cell disease: A 10-year longitudinal study on the SPPIBA cohort
IkeOluwa A.Lagunju, Adeyemi Labaeka, Joy N.Ibeh, Adebola E.Orimadegun, Biobele J.Brown, Olugbemiro O.Sodeinde; (2021)
American Society of Hematology 2020 guidelines for sickle cell disease: prevention, diagnosis, and treatment of cerebrovascular disease in children and adults
M. R. DeBaun, L. C. Jordan, A. King, J. Schatz, E. Vichinsky, C. K. Fox, R. C. McKinstry, P. Telfer, M. A. Kraut, L. Daraz, F. J. Kirkham, M. H. Murad; (2020)
Nocturnal oxyhemoglobin desaturation and arteriopathy in a pediatric sickle cell disease cohort
Nomazulu Dlamini, Dawn E. Saunders, Michael Bynevelt, Sara Trompeter, Timothy C. Cox, Romola S. Bucks, Fenella J. Kirkham; (2017)
Implementation of a Process for Initial Transcranial Doppler Ultrasonography in Children With Sickle Cell Anemia
Lori E. Crosby, PsyD, Naomi E. Joffe, PhD, Blair Davis, MS, Charles T. Quinn, MD, MS, Lisa Shook, MA, Darice Morgan, MSN, Kenya Simmons, MBA, Karen A. Kalinyak, MD; (2016)
Transcranial Doppler ultrasonography (TCD) in infants with sickle cell anemia: baseline data from the BABY HUG trial
Pavlakis SG, Rees RC, Huang X, Brown RC, Casella JF, Iyer RV, et al.; (2010)
Primary stroke prevention for sickle cell disease in north-east Italy: The role of ethnic issues in establishing a Transcranial Doppler screening program
Colombatti R, Meneghetti G, Ermani M, Pierobon M, Sainati L. (2009)
The natural history of conditional transcranial Doppler flow velocities in children with sickle cell anaemia
Hankins JS, Fortner GL, McCarville MB, Smeltzer MP, Wang WC, Li C-S, et al. (2008)
Big strokes in small persons
